HepaGam B® [Hepatitis B Immune Globulin Intravenous (Human)] is approved by the FDA, based on a pivotal clinical study, to prevent HBV recurrence following liver transplantation in HBsAg-positive patients2-4
A significantly lower rate of HBV recurrence following liver transplantation (8.3% vs 85.7% for historical controls (p<.001))2
-
- Recurrence was defined as the development of detectable serum HBsAg and/or HBeAg between Days 28 and 365 following liver transplant (LT)5
Proportion of patients with HBV recurrence
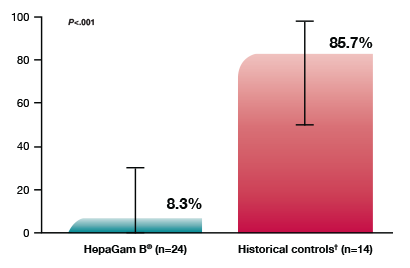
Survival advantage documented in secondary end-point analysis5
HepaGam B® has shown a one-year survival benefit (96% vs. 43% for retrospective control patients)2
Two adverse reactions were observed in clinical trial subjects
who received HepaGam B®—hypotension and nausea2
For more information on Adverse Events, please see the full Prescribing Information.
Clinical trial in liver transplant patients2
The effectiveness of HepaGam B® in the prevention of hepatitis B recurrence following liver transplantation was studied in a multi-center, open-labeled, superiority study involving HBsAg-positive/HBeAg-negative liver transplant patients. The study arms included:
An active treatment group (n=27) enrolled to receive HepaGam B® starting during transplant and continuing over the course of a year
A retrospective untreated control group (n=14) of historical patients with data gathered by chart review
HepaGam B® Dosing Regimen for HBV-Related Liver Transplant Patients (Intravenous)2
Anhepatic Phase |
Week 1 Post-Operative |
Week 2-12 Post-Operative |
Month 4 Onwards |
First dose |
Daily from Day 1-7 |
Every two weeks from Day 14 |
Monthly |
Dosage volume is consistent with published protocols2,6
The FDA approval of HepaGam B® for the prevention of hepatitis B recurrence following liver transplantation in HBsAg-positive patients is based on the dose of 20,000 IU used in the pivotal clinical trial
-
- Total dose should be calculated based on the measured potency stamped on each 5 mL vial label. This provides a dose that is consistent with published protocols. Please note this dosing guidance is specific to HepaGam B®.
HepaGam B® Intravenous Infusion Rate‡
Route of Administration |
Dosage |
Infusion Rate |
Intravenous |
20,000 IU per dose |
2 mL/minute |
Decrease to 1 mL/minute or slower if the patient develops discomfort or infusion-related adverse reactions |
‡HepaGam B dose adjustments may be required in patients who fail to reach anti-HBs levels of 500 International Units per liter within the first week post-liver transplantation. Patients who have surgical bleeding or abdominal fluid drainage (>500 milliliters) or patients who undergo plasmapheresis are particularly susceptible to extensive loss of circulated anti-HBs. In these cases, the dosing regimen should be increased to a half-dose (10,000 International Units calculated from the measured potency as stamped on the vial label) intravenously every 6 hours until the target anti-HBs is reached.2
Dosing Calculation Example
Recommended Dose of HepaGam B® |
Potency |
Calculation |
Based on the 20,000 IU dose in the FDA-approved labeling |
571 IU/mL |
Target dose ÷ measured potency = number of mL |
20,000 IU ÷ 571 IU/mL = 35 mL |
*Round up to nearest full vial
Total dose should be calculated based on the measured potency stamped on each 5 mL vial label. This provides a dose that is consistent with published protocols. Please note this guidance is specific to HepaGam B®.
SELECTED IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
HepaGam B® is a sterile solution of gamma globulin (IgG) made from human plasma. Products made from human plasma may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, eg. viruses and, theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease (CJD) agent.

