Measured dosing
A potency of 550 IU/mL of anti-HBs is targeted at the time of manufacture1
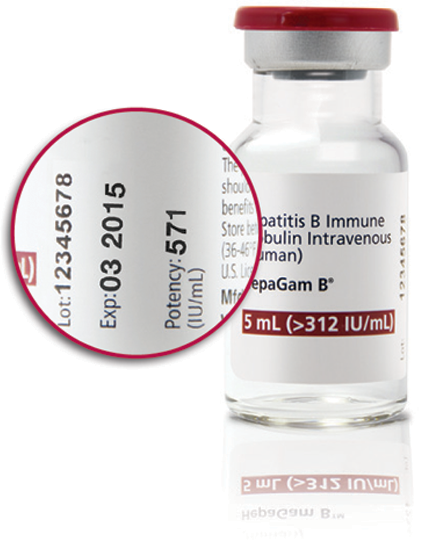
Measured potency: The only HBIg with actual potency stamped on each vial

For prevention of HBV recurrence following liver transplantation:
HepaGam B® combines infusion with precise dosing
HepaGam B® is the only HBIg for the prevention of HBV recurrence following liver transplantation in HBsAg-positive patients that offers:
Infusion times for a 20,000 IU dose1
-
- At 2 mL/minute, the infusion of HepaGam B® takes as little as 20 minutes per patient*
- ~45 minutes for a dose diluted with 50 mL of Normal Saline and infused at a rate of 2 mL per minute
HepaGam B® Dosing Regimen for HBV-Related Liver Transplant Patients
Anhepatic Phase |
Week 1 Post-Operative |
Week 2-12 Post-Operative |
Month 4 Onwards |
First dose |
Daily from Day 1-7 |
Every two weeks from Day 14 |
Monthly |
*Based on a 20,000 IU dose with a total infusion volume of 35 mL at a rate of 2 mL per minute; volume of the dose will vary based on potency. The infusion rate should be decreased to 1 mL per minute or slower if the patient develops discomfort, infusion-related adverse events or if there is concern about the speed of infusion.1
Dosage volume is consistent with published protocols1,2
The FDA approval of HepaGam B® for the prevention of hepatitis B recurrence following liver transplantation in HBsAg-positive patients is based on the dose of 20,000 IU used in the pivotal clinical trial
-
- Total dose should be calculated based on the measured potency stamped on each 5 mL vial label: this provides a dose that is consistent with published protocols
HepaGam B® Intravenous Infusion Rate‡
Route of Administration |
Dosage |
Infusion Rate |
Intravenous |
20,000 IU per dose |
2 mL/minute |
Decrease to 1 mL/minute or slower if the patient develops discomfort or infusion-related adverse reactions |
‡HepaGam B dose adjustments may be required in patients who fail to reach anti-HBs levels of 500 International Units per liter within the first week post-liver transplantation. Patients who have surgical bleeding or abdominal fluid drainage (>500 milliliters) or patients who undergo plasmapheresis are particularly susceptible to extensive loss of circulated anti-HBs. In these cases, the dosing regimen should be increased to a half-dose (10,000 International Units calculated from the measured potency as stamped on the vial label) intravenously every 6 hours until the target anti-HBs is reached.1
Dosing Calculation Example
Recommended Dose of HepaGam B® |
Potency |
Calculation |
Based on the 20,000 IU dose in the FDA-approved labeling |
571 IU/mL |
Target dose ÷ measured potency = number of mL |
20,000 IU ÷ 571 IU/mL = 35 mL |
ΔRound up to nearest full vial
Total dose should be calculated based on the measured potency stamped on each 5 mL vial label. This provides a dose that is consistent with published protocols. Please note this guidance is specific to HepaGam B®.
For HBV post-exposure prophylaxis in the following settings1:
HepaGam B® Dosing Regimen for Post-exposure Prophylaxis (Intramuscular)
Indication |
Dosing |
Instructions |
Acute Exposure to Blood Containing HBsAg |
0.06 mL/kg |
Administer HepaGam B® as soon as possible after exposure. The value after seven days following exposure is unclear. |
For persons who refuse Hepatitis B vaccine or who are known non-responders to vaccine, give a second dose of HepaGam® one month after the first dose. |
||
Perinatal Exposure of Infants Born to HBsAg-Positive Mothers |
0.5 mL |
Administer after physiologic stabilization of the infant and preferably within twelve hours of birth. Administer concurrently with Hepatitis B vaccine. |
Sexual Exposure to HBsAg-Positive Persons |
0.06 mL/kg |
Administer HepaGam B® and Hepatitis B Vaccine series within 14 days of sexual contact or if sexual contact with the infected person will continue. |
Household Exposure to Person with Acute HBV Infection |
0.5 mL |
For infants less than twelve months of age administered concurrently with Hepatitis B Vaccine. Prophylaxis of other household contacts of persons with acute HBV infection is not indicated unless there is an identifiable blood exposure to the index patient, such as by sharing toothbrushes or razors. Treat such exposures like sexual exposures. |

